Programming Environment
Introduction
The ARKA supercomputer at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune operates as a high-performance computing system supporting a variety of scientific and research activities. Users can utilize a flexible programming environment tailored for efficient computation.
Users can manage their programming environment using the 'module' command. For instance:
source Environment:

Examples
| module list | //Show list of already loaded modules |
|---|---|
| module avail | //Show list of available dynamically loadable modules |
| module show [module name] | //this shows the environment paths for given module |
| module load [module name] | //to load a specified module to current environment |
| module unload [module name] | //to unload a specified module from current environment |
| module help [module name] | //to help about required module |
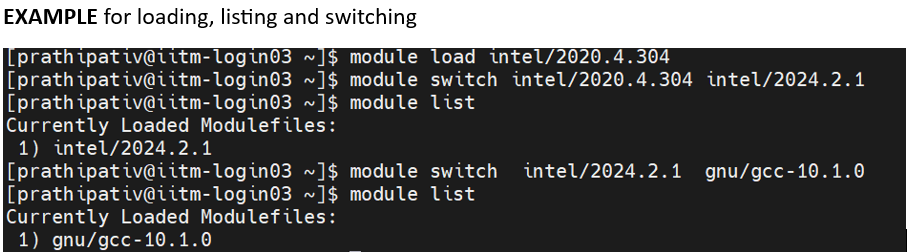
Switching Modules
The module switch command allows you to change from one module to another, which is particularly useful when switching compilers or environments.
module switch [module_old] [module_new]To run GNU-based jobs, switch to the GNU programming environment, adjust the GCC version, and load the necessary modules. The general syntax for switching modules is:
To run jobs with the GNU programming environment, switch to a specific version of GCC (e.g., 9.3.0). Here’s an example:
module list // Shows a list of currently loaded modules
module avail // Lists available modules
module switch gcc/9.3.0 // Switch to GCC version 9.3.0
module unload gcc // Unloads the current GCC compiler
module load gcc/9.3.0 // Loads the new version of GCC